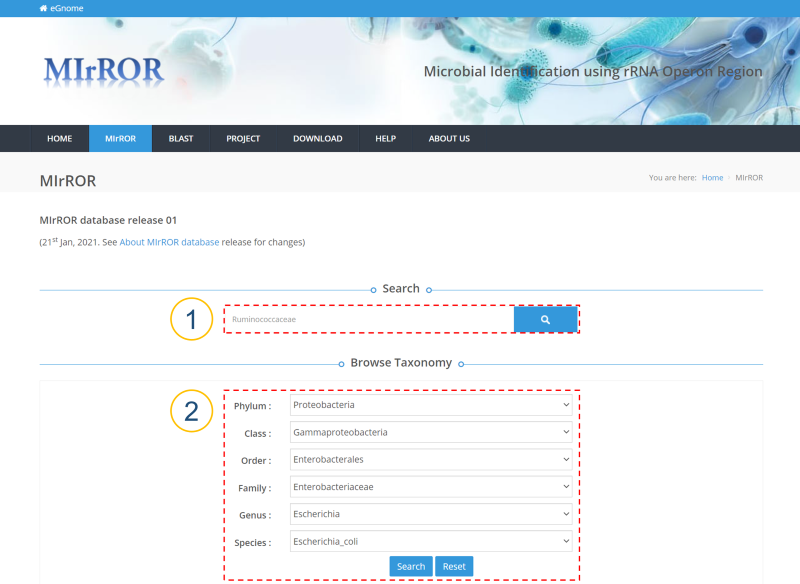
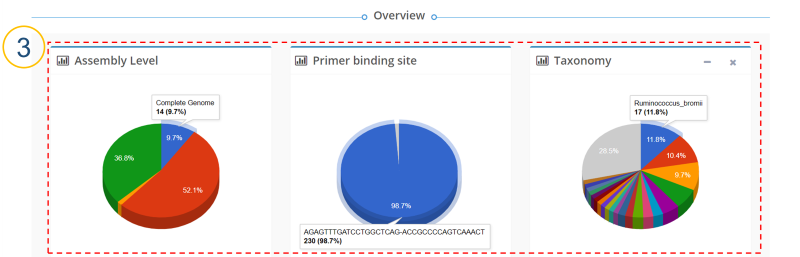
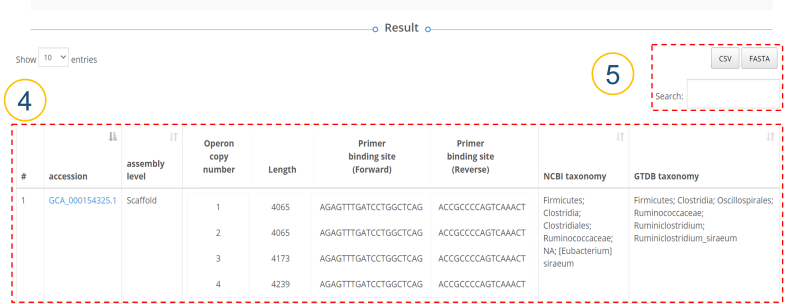
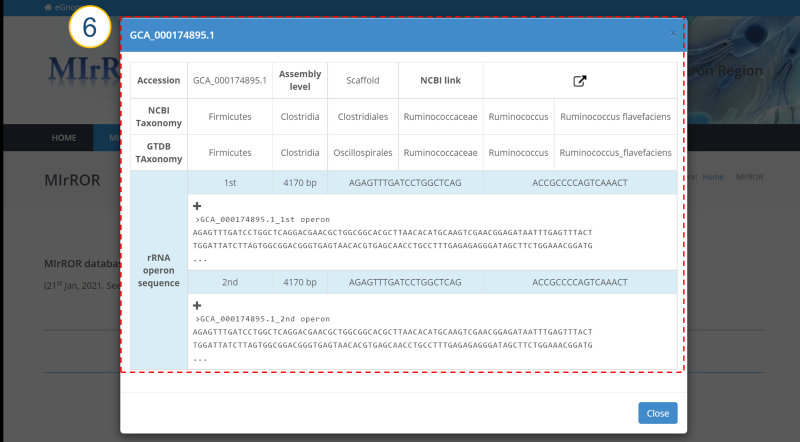
MIrROR is a platform built to enable metagenomics analysis using 16S-23S rRNA operon sequences. MIrROR provides a manually curated database for bacterial 16S-23S rRNA operon sequence and analysis tool that profiles bacterial communities based on mapping strategy. It also provides taxonomic profiling results for the 16S-23S rRNA operon study on NCBI BioProject.
MIrROR was built primarily for metataxonomics and collected sequences based on 27F/2241R, which is most commonly used in 16S-23S rRNA operon analysis. If you use PCR primer that targets the interior region of PCR products from 27F/2241R, you can use MIrROR database without any problems. However, if the reverse primer is located further to the right than 2241R primer, only information except for the region added to the right can be analyzed using MIrROR. If a new PCR primer is introduced and used frequently, it will be reflected in the MIRROR database release update.
Recent studies have shown that there are species whose operon system is broken by the separation of the 16S rRNA gene and the 23S rRNA gene. This includes
Helicobacter, Buchnera, Borrelia, Rickettsia, Thermus, Wolbachia, etc. (See
here for more details on unlinked rRNA genes.)